Publications conjointes CRIBL / Centre National de Référence Amylose AL
Le laboratoire CRIBL et en particulier l’équipe Développement lymphocytaire B terminal et pathologies associées à la sécrétion d’immunoglobulines monoclonales dirigée par Christophe Sirac vient de publier 4 articles conjointement avec le Centre National de Référence Amylose AL dans les prestigieuses revues que sont Blood et Kidney International :
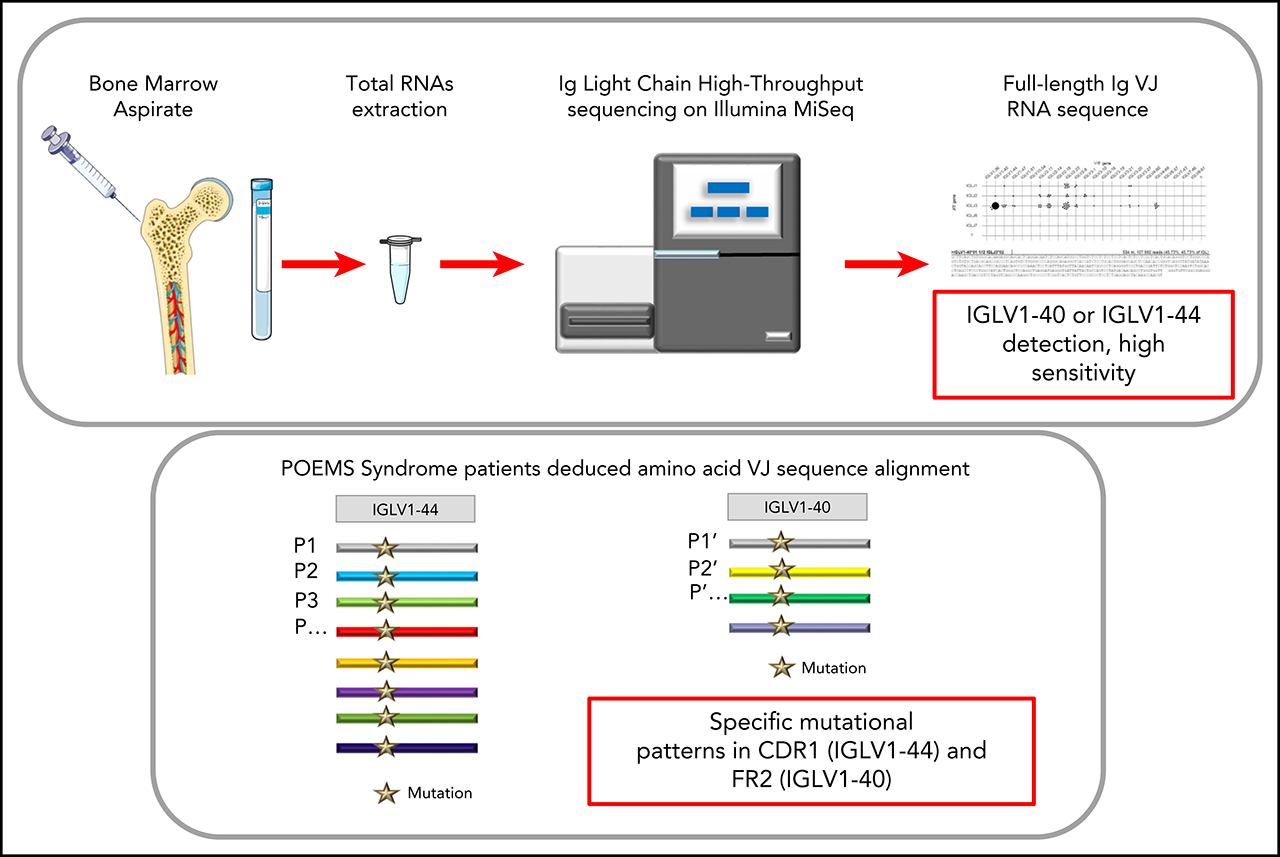
Immunoglobulin Variable Domain High-Throughput Sequencing Reveals Specific Novel Mutational Patterns in POEMS Syndrome
Corresponding author : Christophe Sirac
Affiliations
- 1 Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique UMR CNRS 7276/INSERM U1262, Université de Limoges, France
- 2 Centre National de Référence de l’Amylose AL et autres Maladies par Dépôts d’Immunoglobulines Monoclonales, Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Limoges, France.
- 3 Service d’Immunologie et Immunogénétique, Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Limoges, France
- 4 Service de Néphrologie et Transplantation, Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Poitiers, France
- 5 Etablissement Français du Sang Bretagne, PlateForme de Biotechnologies Innovantes (PFBI), Rennes, France
- 6 Laboratoire d’hématologie biologique, Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Limoges, France
- 7 Service d’Hématologie Clinique, Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Limoges, France
- PMID: 32243509
- DOI: 10.1182/blood.2019004197
Key Points
- RNA-based Ig repertoire sequencing (RACE-RepSeq) is a highly sensitive approach to detect low-abundance POEMS syndrome-related clones.
- RACE-RepSeq with full-length Ig light chain variable domain sequencing reveals specific mutational patterns in POEMS syndrome.
Abstract
POEMS syndrome is a rare multisystem disease due to an underlying plasma cell (PC) dyscrasia. The pathophysiology of the disease remains unclear but the role of the monoclonal immunoglobulin (Ig) light chain (LC) is strongly suspected, due to the highly restrictive usage of two λ variable (V) domains (IGLV1-40 and IGLV1-44) and the general improvement of clinical manifestations following PC clone-targeted treatment. However, the diagnostic value of Ig LC sequencing, especially in case of incomplete forms of the disease, remains to be determined. Using a sensitive high-throughput Ig repertoire sequencing on RNA (RACE-RepSeq), we detected a λ LC monoclonal expansion in the bone marrow (BM) of 83% of patients with POEMS syndrome, including some in whom bone marrow tests routinely performed to diagnose plasma cell dyscrasia failed to detect λ+ monoclonal PCs. Twenty-four of the 29 LC clonal sequences found (83%) were derived from the IGLV1-40 and IGLV1-44 germline genes, two from the closely related IGLV1-36 gene, and all were associated with an IGLJ3*02 junction (J) gene, confirming the high restriction of VJ region usage in POEMS syndrome. RACE-RepSeq VJ full-length sequencing additionally revealed original mutational patterns, the strong specificity of which might crucially help establish or eliminate the diagnosis of POEMS syndrome in uncertain cases. Thus, RACE-RepSeq appears as a sensitive, rapid and specific tool to detect low-abundance PC clones in BM, and assign them to POEMS syndrome, with all the consequences for therapeutic options hereby.
Graphical abstract
Copyright © 2020 American Society of Hematology.
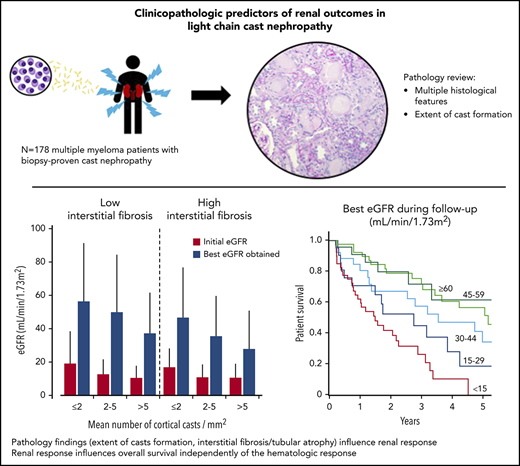
Clinicopathologic Predictors of Renal Outcomes in Light Chain Cast Nephropathy: A Multicenter Retrospective Study
- PMID: 32160635
- DOI: 10.1182/blood.2019003807
Abstract
Light chain cast nephropathy (LCCN) in multiple myeloma often leads to severe and poorly reversible acute kidney injury. Severe renal impairment influences the allocation of chemotherapy, its tolerability, and affects patient survival. Whether renal biopsy findings add to the clinical assessment in predicting renal and patient outcomes in LCCN is uncertain. We retrospectively reviewed clinical presentation, chemotherapy regimens, hematologic response, renal and patient outcomes in 178 patients with biopsy-proven LCCN from 10 centers in Europe and North America. A detailed pathology review, including assessment of the extent of cast formation, was performed to study correlations with initial presentation and outcomes. Patients presented with mean eGFR of 13±11 mL/min/1.73m2, and 82% had stage 3 acute kidney injury. The mean number of casts was 3.2/mm2 in the cortex. Tubulointerstitial lesions were frequent: acute tubular injury (94%), tubulitis (82%), tubular rupture (62%), giant cell reaction (60%), cortical and medullary inflammation (95 and 75%). Medullary inflammation, giant cell reaction and the extent of cast formation correlated with eGFR value at LCCN diagnosis. During a median follow-up of 22 months, mean eGFR increased to 43±30 mL/min/1.73m2. Age, β2-microglobulin, best hematologic response, number of cortical casts/mm2 and degree of interstitial fibrosis/tubular atrophy (IFTA) were independently associated with a higher eGFR during follow-up. This eGFR value correlated with overall survival, independently of the hematologic response. This study shows that extent of cast formation and IFTA in LCCN predicts the quality of renal response which, in turn, is associated with overall survival.
Graphical abstract
Copyright © 2020 American Society of Hematology.
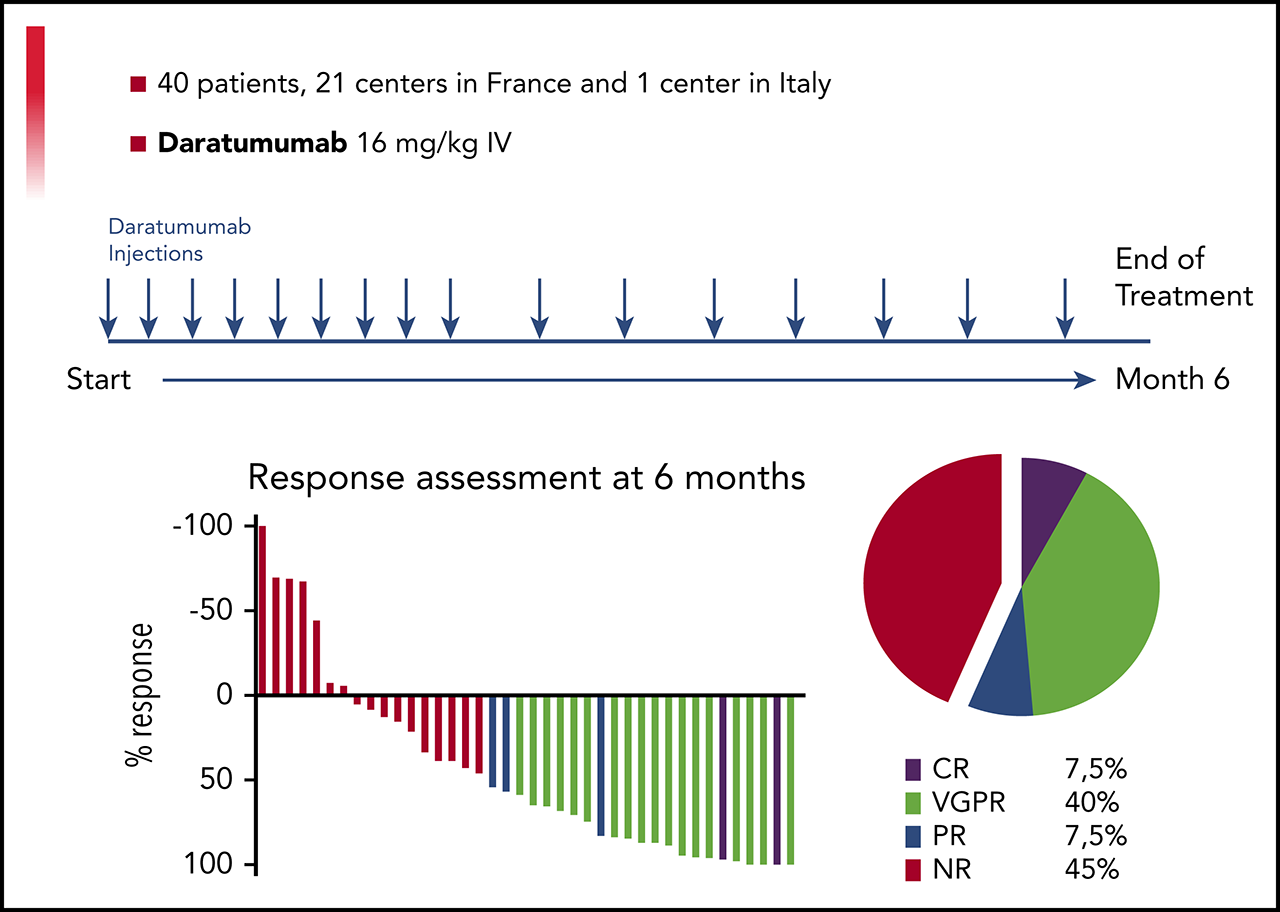
A Prospective Phase II of Daratumumab in Previously Treated Systemic Light Chain Amyloidosis (AL) Patients
- PMID: 32108228
- DOI: 10.1182/blood.2019004369
Abstract
Daratumumab is a human monoclonal antibody targeting CD38, an antigen uniformly expressed by plasma cells in multiple myeloma and light chain amyloidosis (AL). We report the results of a prospective multi-center, phase 2 study of daratumumab monotherapy in AL (NCT02816476). Forty previously treated AL patients with a difference between involved and uninvolved free light chains (dFLC) > 50 mg/L were included in 15 centers between 9/2016 and 4/2018. Patients received six 28-day cycles of IV daratumumab, QW for cycles 1-2 and Q2W for cycles 3-6. Median age was 69 years (range 45-83). Twenty-six patients had 2 or more organs involved with heart in 24 and renal in 26. Median time from diagnosis to enrollment was 23 months (IQR: 4-122) with a median of 3 prior therapies (range 1-5). At data cut-off (09/2019), all patients discontinued therapy and 33 received the planned 6 cycles. Overall, 22 patients had hematological response and 19 patients (47.5%) achieved Very Good Partial Response (dFLC<40mg/l) or better. Median time to hematological response was 1 week. Patients with no response after 4 doses were unlikely to further respond. Renal and cardiac responses occurred in 8 and 7 patients, respectively. Daratumumab was well tolerated with no unexpected adverse events. With a median follow-up of 26 months, the 2-year overall survival rate was 74% (95% CI: 62-81). Daratumumab monotherapy is associated with deep and rapid hematological responses in previously treated AL patients, with a good safety profile. Further studies of daratumumab in combination regimens are warranted.
Graphical abstract
Copyright © 2020 American Society of Hematology.
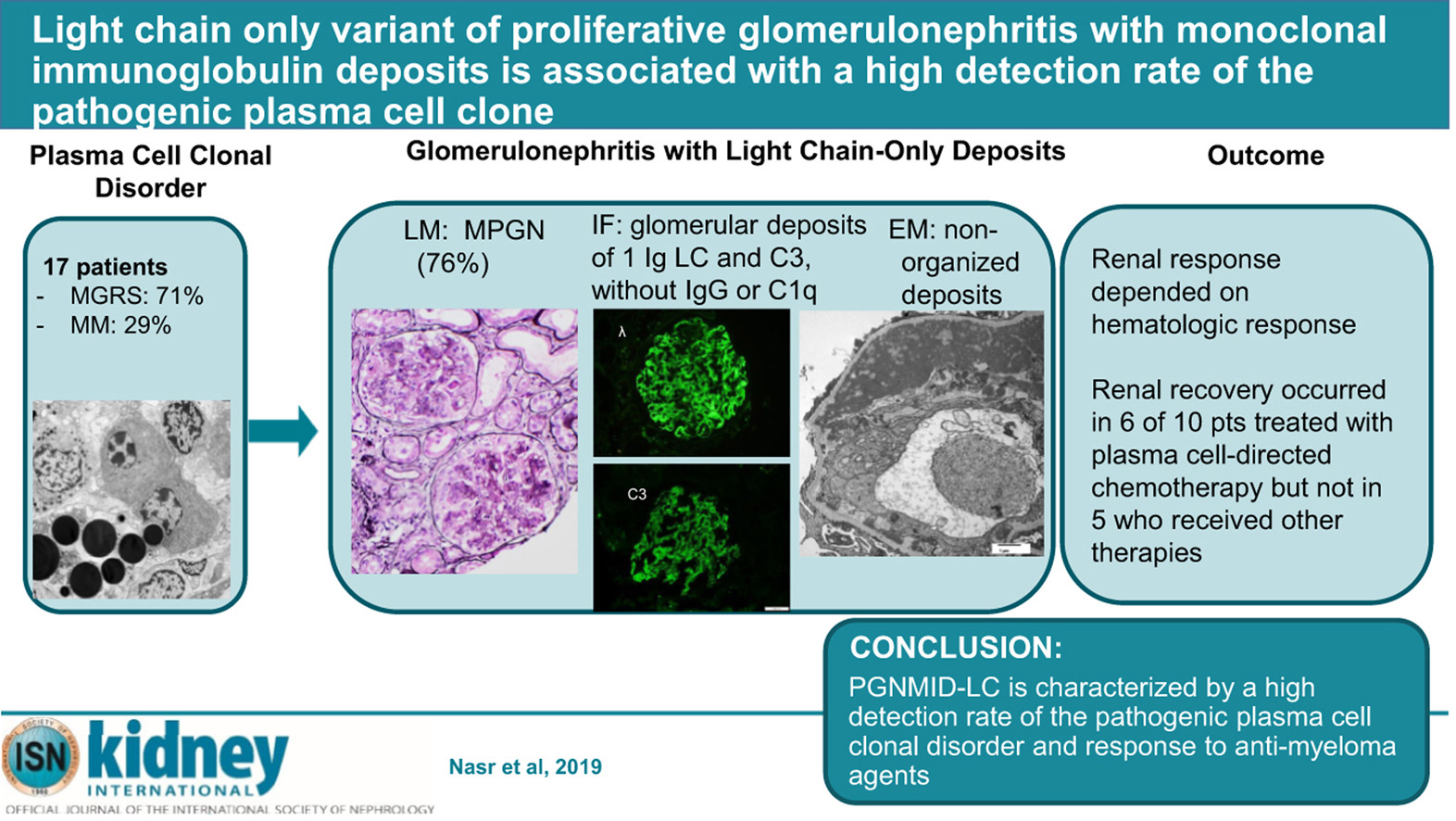
Light Chain Only Variant of Proliferative Glomerulonephritis With Monoclonal Immunoglobulin Deposits Is Associated With a High Detection Rate of the Pathogenic Plasma Cell Clone
Affiliations
- 1 Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, USA. Electronic address: .
- 2 Arkana Laboratories, Little Rock, Arkansas, USA.
- 3 Department of Immunology, Joint Research Unit CNRS 7276, INSERM 1262, University of Limoges, French Reference Center for AL Amyloidosis, University Hospital Dupuytren, Limoges, France.
- 4 Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, USA.
- 5 Department of Nephrology, Dialysis and Renal Transplantation, University Hospital of Poitiers, French Reference Center for AL Amyloidosis, Poitiers, France.
- 6 Assistance Publique-Hôpitaux de Paris, European Hospital Georges Pompidou, Department of Nephrology, Paris, France; INSERM UMRS1138, Research Center Cordeliers, Paris Descartes Sorbonne Paris-Cité University, Paris, France.
- 7 Department of Immunology, Joint Research Unit CNRS 7276, INSERM 1262, University of Limoges, French Reference Center for AL Amyloidosis, University Hospital Dupuytren, Limoges, France; Department of Nephrology, Dialysis and Renal Transplantation, University Hospital of Poitiers, French Reference Center for AL Amyloidosis, Poitiers, France.
- 8 Department of Medicine, Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA.
- 9 Department of Health Sciences Research, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, USA.
- 10 Assistance Publique-Hôpitaux de Paris, Department of Nephrology, Ambroise Paré Hospital, Boulogne-Billancourt, France; Inserm U1018 Team5 UVSQ, University Paris Saclay, Villejuif, France.
- 11 Assistance Publique-Hôpitaux de Paris, Department of Nephrology, Hôpital Tenon, Paris Sorbonne University, Paris, France.
- 12 Assistance Publique-Hôpitaux de Paris, Department of Pathology, Hôpital Tenon, Paris Sorbonne University, Paris, France.
- 13 Department of Nephrology, Bourg-en-Bresse General Hospital, Bourg-en-Bresse, France.
- 14 Department of Nephrology, Roubaix General Hospital, Roubaix, France.
- 15 Department of Pathology and Cell Biology, Columbia University Medical Center, New York, New York, USA.
- 16 Division of Nephrology and Hypertension, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, USA.
- PMID: 32001067
- DOI: 10.1016/j.kint.2019.10.025
Abstract
IgG (mainly IgG3) is the most commonly involved isotype in proliferative glomerulonephritis with monoclonal immunoglobulin deposits (PGNMID). Here we describe the first series of PGNMID with deposition of monoclonal immunoglobulin light chain only (PGNMID-light chain). This multicenter cohort of 17 patients presented with nephritic or nephrotic syndrome with underlying hematologic conditions of monoclonal gammopathy of renal significance (71%) or multiple myeloma (29%). Monoclonal immunoglobulin was identified by serum and urine immunofixation in 65% and 73%, respectively, with abnormal serum free light chain in 83%, and a detectable bone marrow plasma cell clone in 88% of patients. Renal biopsy showed a membranoproliferative pattern in most patients. By immunofluorescence, deposits were restricted to glomeruli and composed of restricted light chain (kappa in 71%) and C3, with granular appearance and subendothelial, mesangial and subepithelial distribution by electron microscopy. Proteomic analysis in four cases of kappa PGNMID-light chain revealed spectra for kappa constant and variable domains, without evidence of Ig heavy chains; spectra for proteins of the alternative pathway of complement and terminal complex were detected in three. The classical pathway was not detected in three cases. After median follow up of 70 months, the renal response was dependent on a hematologic response and occurred in six of ten patients treated with plasma cell-directed chemotherapy but none of five patients receiving other therapies. Thus, PGNMID-light chain differs from PGNMID-IgG by higher frequency of a detectable pathogenic plasma cell clone. Hence, proper recognition is crucial as anti-myeloma agents may improve renal prognosis. Activation of an alternative pathway of complement by monoclonal immunoglobulin light chain likely plays a role in its pathogenesis.
Keywords: MGRS; complement alternative pathway; membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis; monoclonal gammopathy; myeloma.
Graphical abstract
Copyright © 2019 International Society of Nephrology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.