The Ruthven adsorption isotherm is defined by the following equation:
where b is the equilibrium binding constant, c the concentration
of the adsorbate in solution, x = q / qs, q is the adsorbed quantity
and qs a scaling parameter. Ei is the
exponential integral :
The Ruthven equation is solution of the differential equation:
|
|
d lnq
d lnc
|
= exp(− q / qs) |
|
So, the slope of the isotherm in log-log coordinates decreases exponentially when q increases
(for the Freundlich isotherm, the slope is constant)
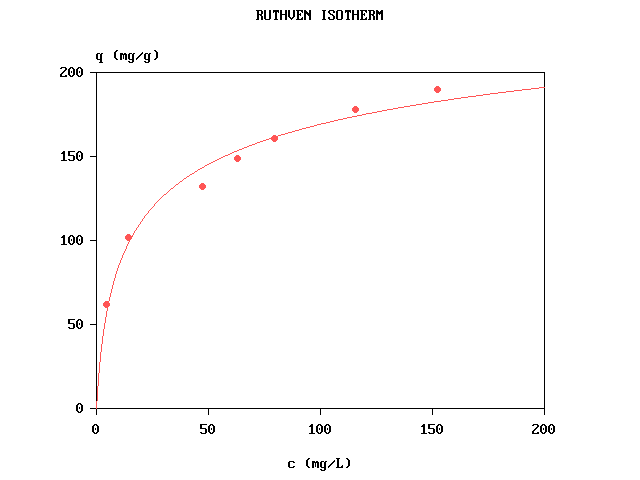
Fitting the Ruthven isotherm
The computer program Ruthven.bas written in FreeBASIC fits the curve by nonlinear
regression, using simulated annealing followed by Marquardt's method. The fitted parameters are
qs and b.
Reference
K. H. Chu, M. A. Hashim, A. Mudhoo, J. Debord,
Beyond Freundlich and Langmuir: the Ruthven–virial equilibrium isotherm for aqueous‑solid adsorption systems.
Chemical Papers, 2022.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-022-02576-4

